Tidecoin uses FALCON as the signature algorithm for the signature. FALCON uses a lattice-based approach.
This article aims to briefly outline what mathematical problem is behind the encryption and why it is so powerful, also against quantum computers
Two vectors are given.
Integer numbers are used for the factors z. Therefore, a grid structure (lattice) results. Hence the name lattice based encryption. You can see an illustration in the document.
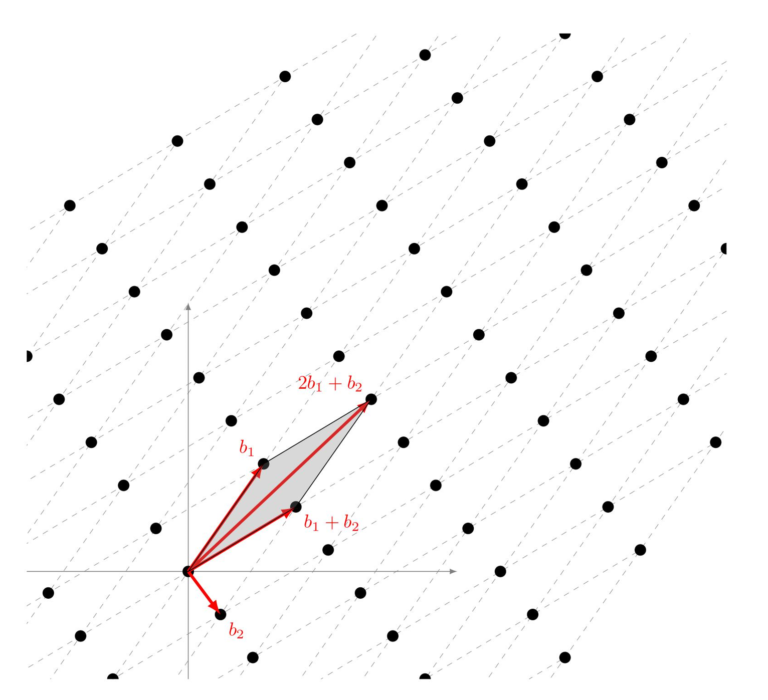
Let us try an example with real values for the vectors b.
The following vector is now choosen randomly. Constraint is, it must not be a multiple of the vector equation and the vector must be an integer.
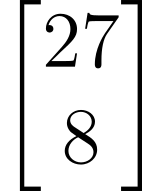
The goal is to find the smallest distance to the vector for the given points from the upper lattice structure (closest vector problem). We can set up a system of equations for this. However, we notice that we have two variables and two equations. So it might be easy to solve by using a calculator.
Both values for z must be rounded to an integer so that we end up on a grid point after solving the equation.
We are calculating the grid point with the rounded values for z and the vectors.
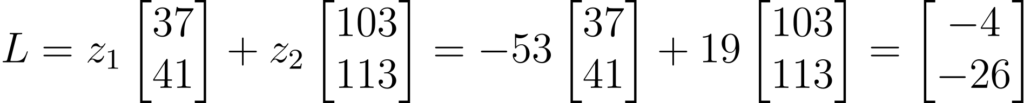
The calculated lattice point is far away and certainly not the nearest neighbor of the choosen vector (27, 8).
Even if we substitute z1 = 1 and z2 = 0 from our considerations, we get (37, 41) as a lattice point. This lattice point is closer than the calculated point.
This mathematical problem is very difficult to solve. Quantum computers will have no advantage over analogue computers here.
Lattice-based encryption, including the FALCON signature, is based on this approach.
FALCON is used by Tidecoin to protect wallets from attacks by the quantum computer.
